前言
最近在整理 SimpleRNN、LSTM 與 GRU 這三種方法的差別,按照其定義三種參數量的比例為 1:4:3。 但是經過實際程式執行測試後發現 Tensorflow 在 2.X 執行下參數量竟然不是 SimpleRNN 的 3 倍!? 詳細內容可以參考我在 Tensorflow GitHub 上的 issue。最後才發現原來 GRU 在 Tensorflow 2.X 中將 reset_after=True 做為預設,因此每個計算過程中會有獨立出來的偏權值(bias)。這個屬性是做什麼的?下面就來幫各位解惑。
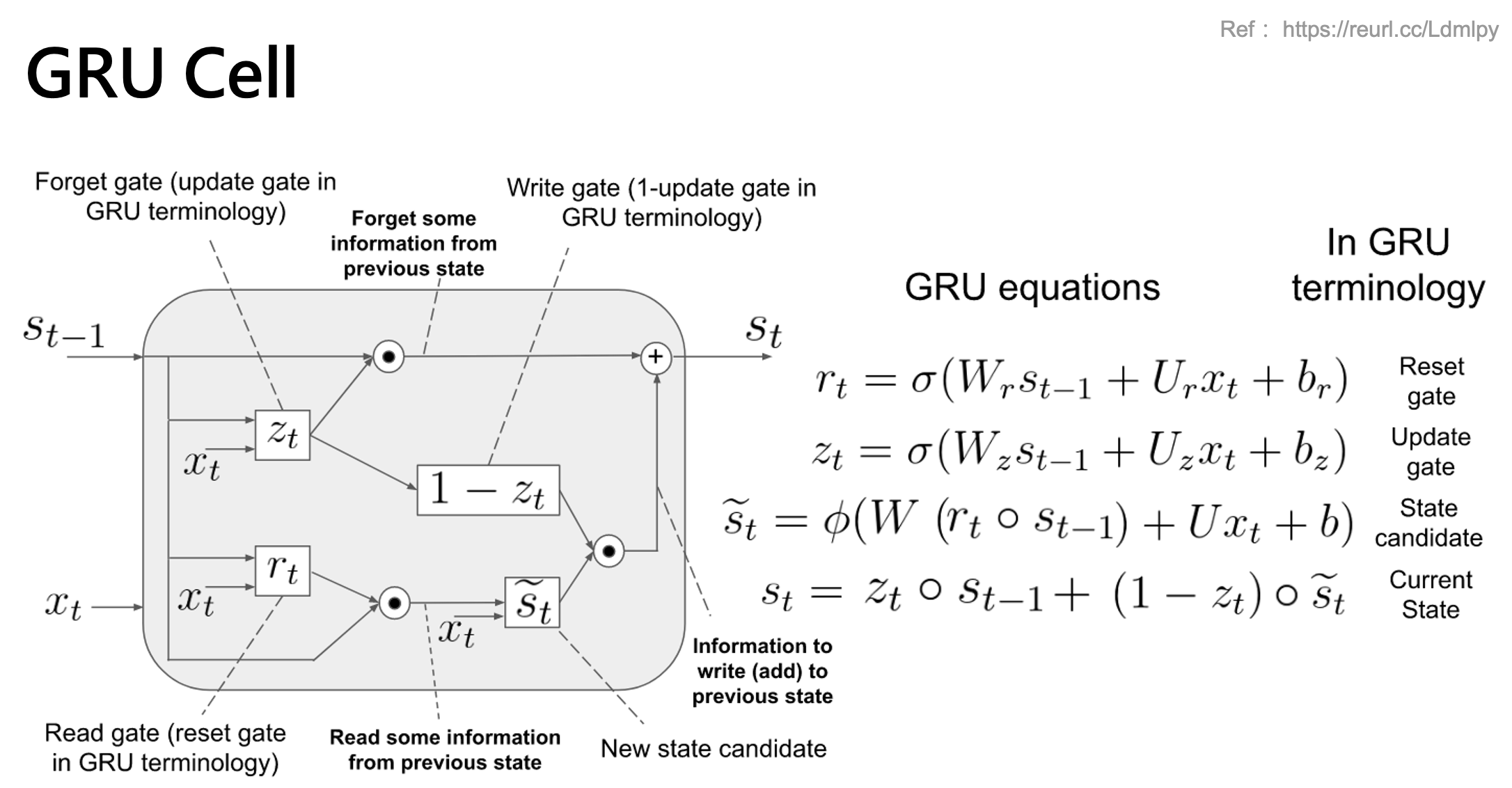
GRU 權重計算
以下範例我們分別在 tensorflow 1.X 與 2.X 環境下測試相同的程式,透過 summary() 可以查看神經網路的架構以及每一層的參數量及總參數量。以下範例程式我們建立一層的 GRU 隱藏層,其輸入為 windows size 10,也就是有 10 筆的時序資料。每一筆資料內有 4 個特徵。RNN 的優點就是不同的時間點資料共用同一組權重,因此在計算權重數量時 windows size 不予參考。計算 GRU 的參數量很簡單,其實就是 SimpleRNN 的三倍,為什麼是三倍呢?因為 GRU 多了兩個 Gate (input gate & reset gate)。基本 GRU 的權重數量計算方式如下:
- params = 3 * [ (dh + dx + b) * dh ]
- 150 = 3 * [ (4 + 5 + 1) * 5]
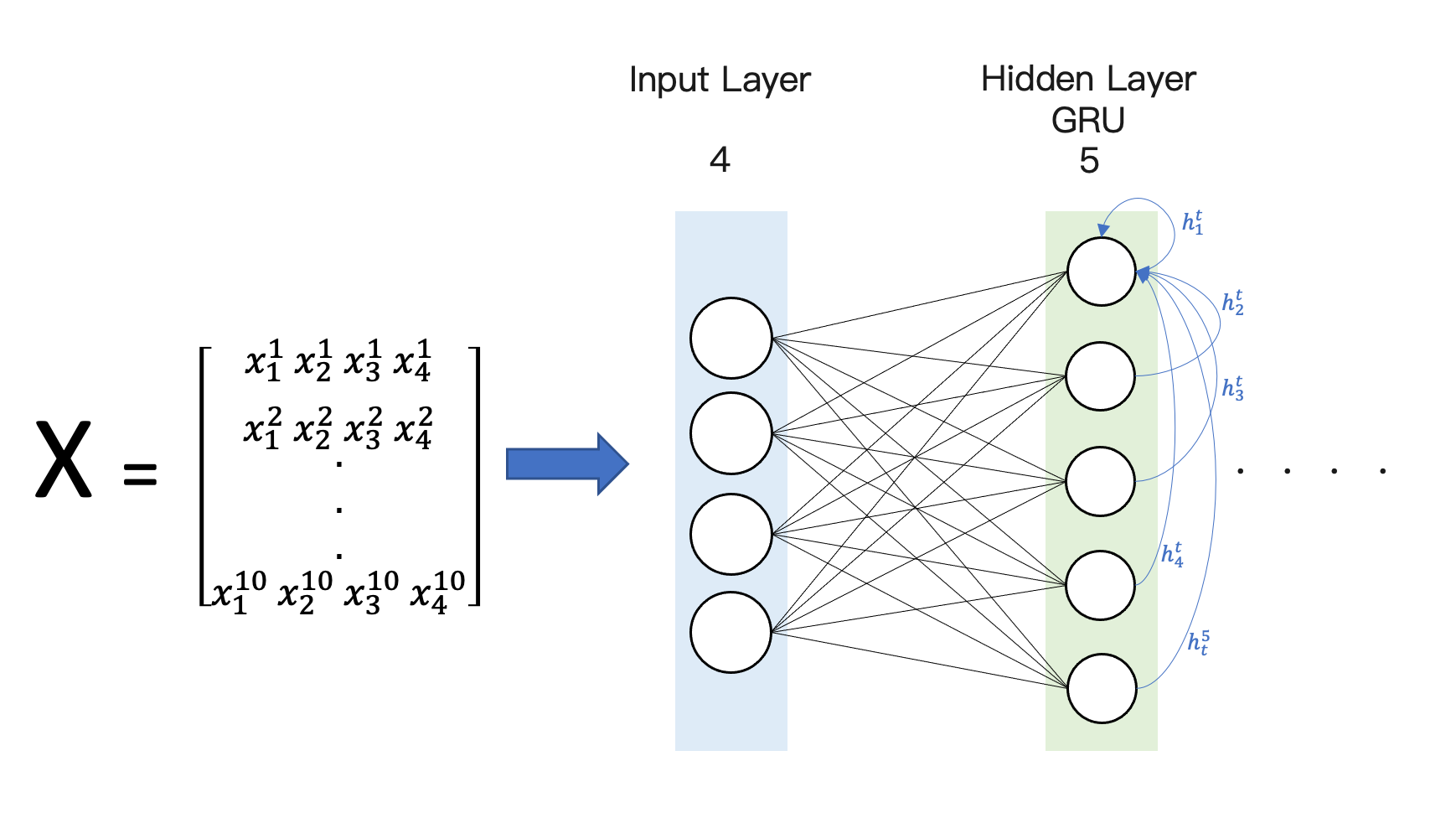
dh 為隱藏層的維度,也就是隱藏層神經元數量,範例中為 5,dx 為輸入特徵的數量,範例中設為 4。下面的範例程式中有一層的 GRU 網路層,其神經元數量有 5 個。我們目標就是要計算圖中所有的神經元連線的數量,藍色線條為隱藏層第一個神經元的線條流向(其他的cell概念一樣)。也就是隱藏層這一次的 hidden state 輸出結果會留給下一次當作輸入特徵使用。因此每一個 cell(神經元) 除了接收上一次自己的輸出,還包括其他鄰居的 cell 的輸出(hidden state) 當作這一個 cell 下一次的輸入。
GRU in Tensorflow 1.X
我們來看一下 GRU 在 Tensorflow 1.X 環境下執行結果。可以發現權重數量跟我們上述的公式計算結果相符。
from keras import Model, Input
from keras.layers import GRU
input = Input(shape=[10, 4])
gru = GRU(5)(input)
model = Model(input, gru)
model.summary()
Model: "model_2"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_2 (InputLayer) (None, 10, 4) 0
_________________________________________________________________
gru_2 (GRU) (None, 5) 150
=================================================================
Total params: 150
Trainable params: 150
Non-trainable params: 0
GRU in Tensorflow 2.X
一樣的程式碼我們在 Tensorflow 2.X 環境下執行可以發現參數量竟然不同!?這是什麼問題呢?其原因是在 Tensorflow 2.X 版本將 reset_after=True 設為預設,但在 1.X 版本預設是 False。這個參數設定 True 的話代表權重能與 CuDNNGRU 模型共用。CuDNNGRU 模型主要是透過 GPU 加速訓練。如果訓練好後想利用 GRU 架構的 CPU 推論的話需要設定 reset_after=TrueCuDNNGRU 的權重數量計算方式如下:
- params = 3 * [ (dh + dx + b + b) * dh ]
- 165 = 3 * [ (4 + 5 + 1 + 1) * 5]
from keras import Model, Input
from keras.layers import GRU
input = Input(shape=[10, 4])
gru = GRU(5)(input)
model = Model(input, gru)
model.summary()
Model: "functional_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 10, 4)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
gru (GRU) (None, 5) 165
=================================================================
Total params: 165
Trainable params: 165
Non-trainable params: 0
GRU 的 reset_after 屬性
首先我們要來談談 CuDNNGRU,雖然 GRU 在 GPU 上效能沒有很大幅提升。因為 RNN 的性質難以平行化,然而在 CuDNNGRU 為了加速計算因此計算方式與一般 RNN 有稍微不同。間單來說 CuDNNGRU 在 Xt 與 h(t-1) 將會各自獨立的 b(偏權值)。Xt、h(t-1) 在一般的 RNN 是共用 b 的,但是在 CuDNNGRU 中 b 是各自獨立的。下面我們以 reset gate 舉例:
-
一般的 GRU 計算方式是這樣
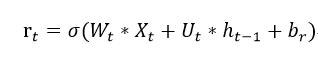
-
CuDNNGRU 的 reset gate 是這樣計算
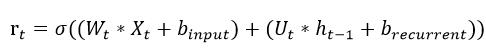
由上面兩個公式可以發現 CuDNNGRU 在計算上動了什麼手腳嗎?沒錯多了一組 bias。原本輸入的 X 與遞迴的 h 是共用一組 b 但是在 GPU 運算時 b 是分開各自獨立的。其他的 update gate 與 S 的計算跟上述概念一樣,計算時也是各自獨立 b。然而在 Tensorflow 2.X 的 GRU 為了要與 CuDNNGRU 相容,並使用 CPU 做推論因此預設 reset_after=True 所以在 Tensorflow 2.X 預設的 GRU 權重數量跟原本論文定義的不同。如果權重數量想 SimpleRNN 的三倍就將 reset_after=False 即可。
from keras import Model, Input
from keras.layers import GRU
input = Input(shape=[10, 4])
gru = GRU(5, reset_after=False)(input)
model = Model(input, gru)
model.summary()
Model: "model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 10, 4)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
gru (GRU) (None, 5) 150
=================================================================
Total params: 150
Trainable params: 150
Non-trainable params: 0
註: Tensorflow 2.X 預設 reset_after=False / Tensorflow 1.X 預設 reset_after=True
Reference
- Keras recurrent layer 官方文檔
- Tensorflow GRU Doc
- stackoverflow
- GitHub issue *thanks jvishnuvardhan and amahendrakar
以下引用 Tensorflow 2.0 官方文件[2]
There are two variants of the GRU implementation. The default one is based on v3 and has reset gate applied to hidden state before matrix multiplication. The other one is based on original and has the order reversed.
The second variant is compatible with CuDNNGRU (GPU-only) and allows inference on CPU. Thus it has separate biases for kernel and recurrent_kernel. To use this variant, set ‘reset_after’=True and recurrent_activation=’sigmoid’.
| Argument | description |
|---|---|
| reset_after | GRU convention (whether to apply reset gate after or before matrix multiplication). False = “before”, True = “after” (default and CuDNN compatible). |
 https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCSNPCGvMYEV-yIXAVt3FA5A
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCSNPCGvMYEV-yIXAVt3FA5A