前言
自 GPT-4 問世以來,「Function Calling」幾乎是所有開發者的入門關鍵字。 而如今,它不再只是「呼叫一個函式」的技術,而是被整合進更大的 Tool Use(工具使用) 生態中。 這場變化不只是改名,而是從「讓模型能呼叫函式」,邁向「讓模型能靈活運用整個工具生態」的思維轉折。
本文將帶大家一次看懂這場變化的脈絡、原因與實務影響。
從「函式呼叫」到「工具使用」的演進
| 時期 | 主流代表 | 名詞 | 核心概念 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 初期 | OpenAI GPT-4、LangChain (早期 Function Agent) | Function Calling | 模型輸出 function_name + arguments;由外部程式執行並回傳結果。 |
| 2023 下半年 | Claude 2.1、Gemini 1.5 | Tool Use/Tools | 模型可呼叫多種外部能力(不限於函式),支援多步決策與串流回傳。 |
| 2024 起 | OpenAI Assistants API、Claude 3、MCP 協定 | Tools 作為標準介面 | 工具可獨立註冊、跨應用共用;模型與工具透過協定(如 MCP)互通。 |
Function Calling 是技術;Tool Use 是語意與架構。 過去我們只是「讓模型會呼叫函式」;現在我們在做的是「讓模型能靈活使用一整個工具生態系」。
在 API 層面的對應關係
在實作上,「Function Calling」與「Tool Use」也反映在 API 欄位名稱的變化:
| 概念層 | Function Calling | Tool Use | 說明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工具宣告 | functions |
tools |
可用函式/工具清單 |
| 模型選擇 | function_call |
tool_calls |
模型實際決定要用哪些(新版支援多個) |
| 使用策略控制 | 無 | tool_choice |
控制模型是否、如何使用工具 |
| 呼叫數量 | 一次一函式 | 可多工具協作 | |
| 範圍 | 僅限程式函式 | 可涵蓋 API、RAG、工作流、MCP 等 |
也就是說: Function Calling 對應到 functions;Tool Use 對應到 tools。
技術演化關鍵
Function Calling 一次只能呼叫一個函式
在 GPT-4 初期與 OpenAI 舊版 Chat Completions API 中,
開發者需預先定義一組或多組 functions,但模型每次回傳時,只能選擇呼叫其中一個函式。
例如(請求):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-0613",
functions=[
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current weather information",
"parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}}}
},
{
"name": "search_news",
"description": "Search latest news",
"parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"keyword": {"type": "string"}}}
},
],
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "幫我查一下今天台北天氣,並找幾篇相關新聞"}
]
)
模型回傳(assistant 訊息片段):
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"function_call": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{ \"location\": \"台北\" }"
}
}
此時它只能執行 get_weather;
若要再呼叫 search_news,必須由外部程式先執行 get_weather、把結果回填成一則 role="function" 的訊息,再進行第二輪推理,模型才可能下一步再呼叫 search_news。
也就是說:Function Calling 是「一次一函式」的同步機制。
而 Tool Use 則支援多工具協作
從 2024 年起(OpenAI Assistants API、Claude 3、Gemini 1.5 之後),
新的 tools 與 tool_calls 格式讓模型能:
- 一次呼叫多個工具;
- 在單一回應中執行多步操作;
- 支援串流(streaming)或異步(async)執行。
例如(請求):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[
{"type": "function", "function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}}}
}},
{"type": "function", "function": {
"name": "search_news",
"parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"keyword": {"type": "string"}}}
}}
],
tool_choice="auto",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "幫我查今天台北天氣並找幾篇相關新聞"}
]
)
模型回傳(assistant 訊息片段):
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_1",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{ \"location\": \"台北\" }"
}
},
{
"id": "call_2",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_news",
"arguments": "{ \"keyword\": \"台北天氣\" }"
}
}
]
}
重點:
tool_choice是輸入端用來控制「是否/如何用工具」;tool_calls是輸出端回傳「實際呼叫了哪些工具」。 新版 Tool Use 支援在一次回應中產生多個tool_calls,形成自然的多工具協作流程。
模型可在一次推理中同時規劃並呼叫多個工具, 實現真正的「多任務 Agent 式」行為。
| 面向 | Function Calling (舊) | Tool Use / Tools (新) |
|---|---|---|
| 每次呼叫 | 一次僅呼叫一個函式 | 一次可呼叫多個工具 |
| 執行方式 | 同步、單步 | 串流、多步、可異步 |
| 接口名稱 | functions + function_call |
tools + tool_calls |
| 設計思維 | API 指令式 | 工具生態式 |
| 應用範例 | LangChain Function Agent | MCP、Assistants API、Dify Tools |
為何業界棄「Function Calling」改用「Tool Use」
1. 語意更廣、可擴充
「Function」太狹隘,只適合單一 API;而「Tool」可代表任何外部能力: API 呼叫、RAG 檢索、MCP 伺服器、資料庫查詢、程式執行、甚至整個 workflow。
2. 多工具協作成常態
現代 Agent 往往同時需要查資料、跑演算法、再生成摘要。 Tool Use 讓模型能在一次推理中挑選並連續使用多個工具,而不是一回合只執行一支 function。
3. 支援標準協定與跨應用重用
MCP (Model Context Protocol) 讓工具能被不同應用共用。 透過標準化 schema 與通訊方式,工具不再綁死在單一 Agent 內。
4. 更好對應新一代 API 格式
- OpenAI v1.2 之後:全面改用
tools、tool_choice欄位,淘汰舊functions。 - Anthropic Claude 3 系列:引入
tool_use事件,可同時多工具串流。 - Gemini 1.5 / Mistral API:沿用 OpenAI 相容格式。
Tool Use 是「統一框架」
在新版 OpenAI、Anthropic Claude 3、Gemini 1.5 乃至 Dify、n8n 等 Agent 系統裡, Tool Use = 模型使用外部能力的通用協定。
這個協定定義了三件事:
| 元素 | 角色 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
tools |
工具清單(輸入) | 告訴模型有哪些工具可用、每個工具的描述與參數結構。 |
tool_choice |
控制策略(輸入) | 決定模型能否、是否要使用工具。 |
tool_calls |
呼叫結果(輸出) | 模型實際決定要使用哪些工具與參數。 |
Tool Use 可包含多種「工具類型」
tools 是一個清單(list),
每個元素都是一個可呼叫的外部能力,且都有 type 欄位。
不同框架可定義不同類型,例如:
類型 (type) |
代表技術 | 用途/說明 |
|---|---|---|
"function" |
Function Calling | 最常見;執行一個程式函式。 |
"retrieval" |
RAG 檢索 | 查詢向量資料庫、知識庫。 |
"code_interpreter" |
程式執行/Python sandbox | 執行代碼、運算、繪圖。 |
"mcp" |
MCP 伺服器(Model Context Protocol) | 從外部協定載入工具、資料或資源。 |
"file_search" |
檔案/文件搜尋工具 | 在已上傳檔案中檢索內容。 |
"browser" |
瀏覽工具 | 讓模型發出 HTTP 請求或檢索網頁。 |
所以 Function Calling 與 MCP 並列為 Tool Use 架構下的不同「tool type」。
我們這裡就以OpenAI Python SDK 做一個範例,同時定義多種工具:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[
# Function Calling 型工具
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "取得天氣資訊",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}}
}
}
},
# MCP 工具(外部伺服器)
{
"type": "mcp",
"server_url": "https://notes-mcp-server.local",
"tools": ["list_notes", "read_note"]
},
# 檔案檢索工具
{"type": "retrieval"}
],
tool_choice="auto",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "幫我讀出最新筆記並查天氣"}]
)
這裡模型可以:
- 透過 Function Calling 呼叫
get_weather(); - 透過 MCP 伺服器呼叫
list_notes()、read_note(); - 若語意需要,也能用
retrieval查知識庫內容。
從設計角度看,簡單用一個表格整理:
| 層級 | 舊架構 | 新架構(Tool Use) |
|---|---|---|
| 語意 | 「模型呼叫函式」 | 「模型靈活使用多種工具」 |
| 技術形式 | functions + function_call |
tools + tool_calls + tool_choice |
| 擴充性 | 只能呼叫函式 | 可掛載任何外部服務或協定(含 MCP) |
實務建議:開發時怎麼跟上這波轉變
-
程式層面
- 若使用 OpenAI 新版 SDK:請改用
tools而非functions。 - LangChain、LangGraph 等框架已全面以 Tool 為核心抽象;MCP 工具可直接掛入。
- 若使用 OpenAI 新版 SDK:請改用
-
命名與文件
- 文件用語建議改成「Tool Use/工具呼叫」。
- 若需兼容舊版,可註記:「即早期 Function Calling 機制(functions 欄位)」。
-
架構層設計
- 把工具定義、執行邏輯抽離應用程式,放進 MCP Server 或共享模組。
- 讓 Agent 只負責決策與流程控制,不直接耦合具體工具。
-
觀測與維運
- 開啟 Tracing (如 LangSmith 或自建 Logger),追蹤各 tool 的延遲、成功率、成本。
- 工具 schema 保持簡潔明確,模型選擇會更穩定。
未來趨勢:從 Tool Use 到可組裝的 Agent 平台
未來的 LLM 應用不再是「一個模型 + 一支函式」的直線流程,而是以 Tool Use 為核心、可自由組裝的多工具工作流(Agentic System)。 這樣的系統以 LLM 為大腦、Tool 為手腳、MCP 等協定為神經網絡,讓模型不僅能回答,更能行動。
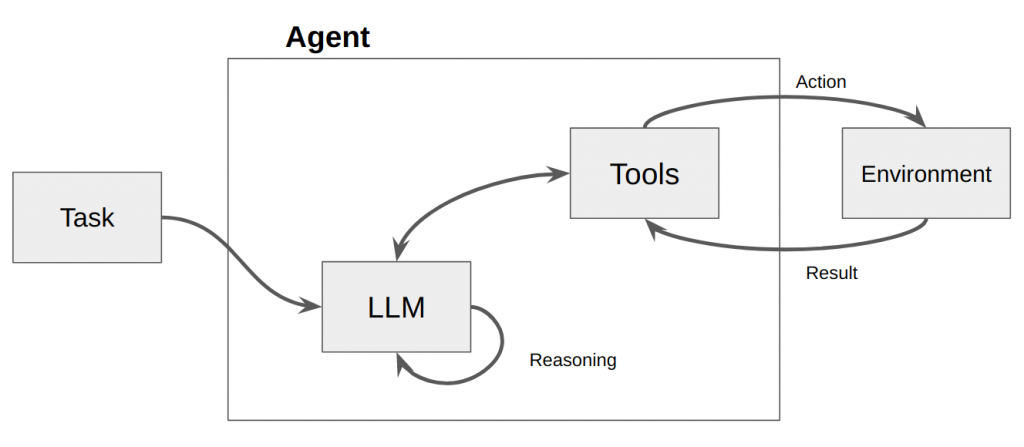
結語
總而言之,Tool Use 並非 Function Calling 的替代品,而是其進化版。
在新版架構中,tools/tool_calls 成為統一介面,舊有的 Function Calling 則以 type: "function" 的形式延續存在。MCP 提供跨應用共享與治理能力,但並非所有專案都必須依賴。 最終目標是打造能「推理並行動」的 Agent。LLM 負責思考,工具負責執行,開發者要做的,是設計出可被 LLM 穩定理解與使用的工具層。
參考
鼓勵持續創作,支持化讚為賞!透過下方的 Like 拍手👏,讓創作者獲得額外收入~ https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCSNPCGvMYEV-yIXAVt3FA5A
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCSNPCGvMYEV-yIXAVt3FA5A